Aave V3 Liquidation Tracker
Monitor and analyze liquidation events on the Aave V3 protocol in real-time. This project demonstrates the power of serverless blockchain data streaming using Quicknode's Streams.
Introduction
Monitor and analyze liquidation events on the Aave V3 protocol in real-time. This project demonstrates the power of serverless blockchain data streaming using Quicknode's Streams.
| Dashboard Overview | Liquidations Table |
|---|---|
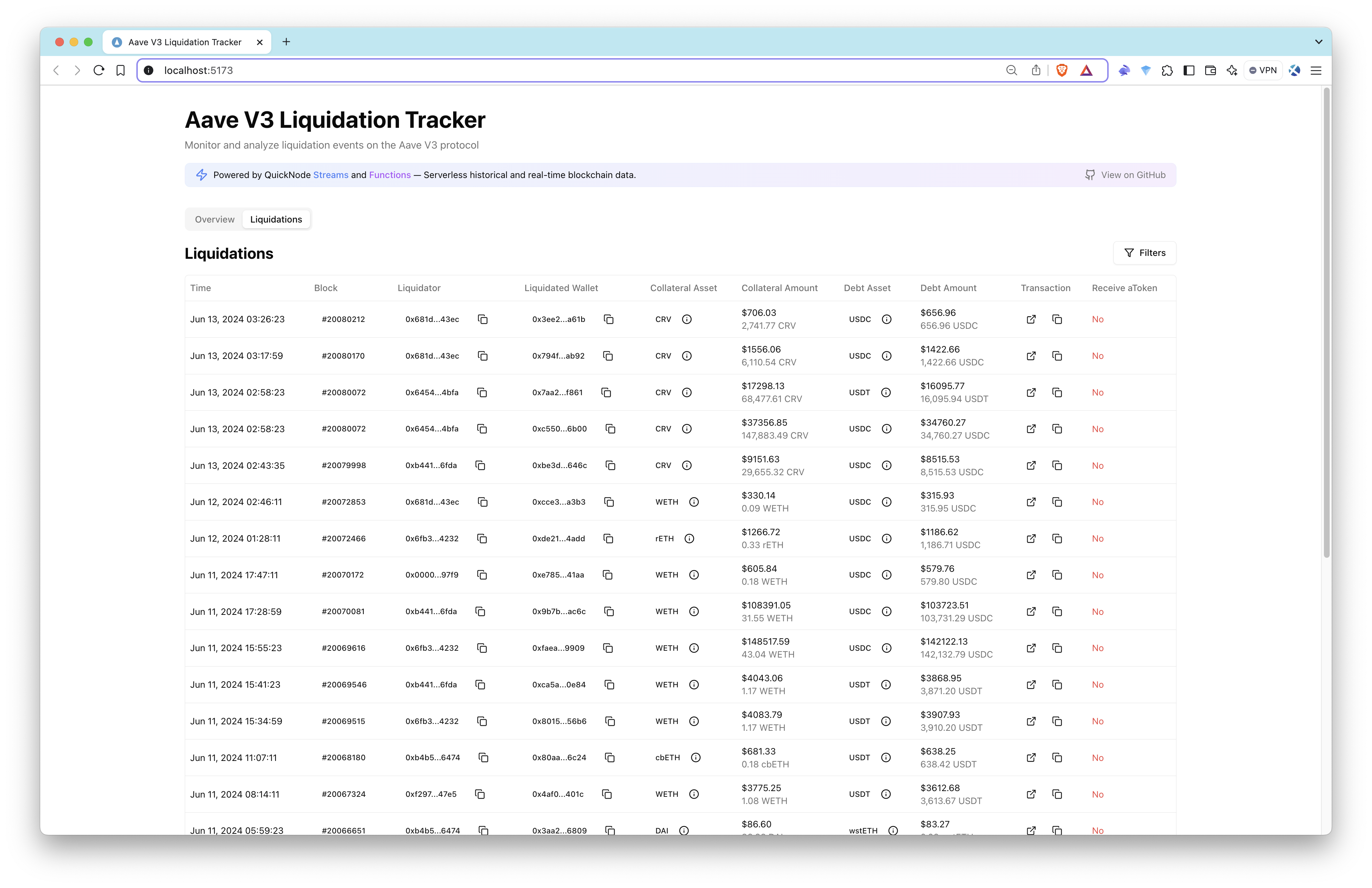 |
Features
- 📊 Real-time liquidation monitoring
- 💰 Detailed metrics and analytics
- 📈 Historical liquidation trends
- 🔄 Asset distribution analysis
- ⚡ Serverless architecture
Aave Pool Contract and LiquidationCall Event
Aave V3 Pool Contract Overview
The Pool.sol contract (For Ethereum Mainnet, 0x87870Bca3F3fD6335C3F4ce8392D69350B4fA4E2) in the Aave V3 protocol is the core of the lending and borrowing system. It facilitates deposits, borrowing, repayments, and liquidations.
Event to Track: LiquidationCall
The LiquidationCall event is emitted when a liquidation occurs in the Aave protocol. It provides critical information about the liquidation transaction, including the collateral seized and the debt repaid.
// Event Signature
// 0xe413a321e8681d831f4dbccbca790d2952b56f977908e45be37335533e005286
LiquidationCall(
address collateralAsset,
address debtAsset,
address user,
uint256 debtToCover,
uint256 liquidatedCollateralAmount,
address liquidator,
bool receiveAToken
)
Event Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
collateralAsset | address | The address of the asset being seized as collateral. |
debtAsset | address | The address of the asset that the liquidator is repaying. |
user | address | The address of the borrower being liquidated. |
debtToCover | uint256 | The amount of debt being repaid during the liquidation. |
liquidatedCollateralAmount | uint256 | The amount of collateral seized by the liquidator. |
liquidator | address | The address of the liquidator performing the liquidation. |
receiveAToken | bool | If true, liquidator receives aTokens instead of collateral. |
We will be using decoded logs of the LiquidationCall event to track liquidations on the Ethereum Mainnet.
How It Works
This application uses a completely serverless architecture to track and analyze Aave V3 liquidation events:
- Data Collection: Streams monitors the raw blockchain event data for Aave V3's liquidation events in both historical and real-time
- EVM Decoding: Streams decode the raw event data using the EVM Decoder to extract the relevant information
- Data Processing: Using
viemand webhooks, we temporarily listen to incoming data and process the decoded event data by fetching token prices and token details - Data Storage: Enriched event data is automatically stored in the PostgreSQL database
- Frontend Display: React application fetches and displays the data with real-time updates
Tech Stack
-
Frontend
- React
- TypeScript
- TanStack Query for data fetching
- Tailwind CSS for styling
- shadcn/ui for UI components
- Recharts for data visualization
-
Backend
Architecture
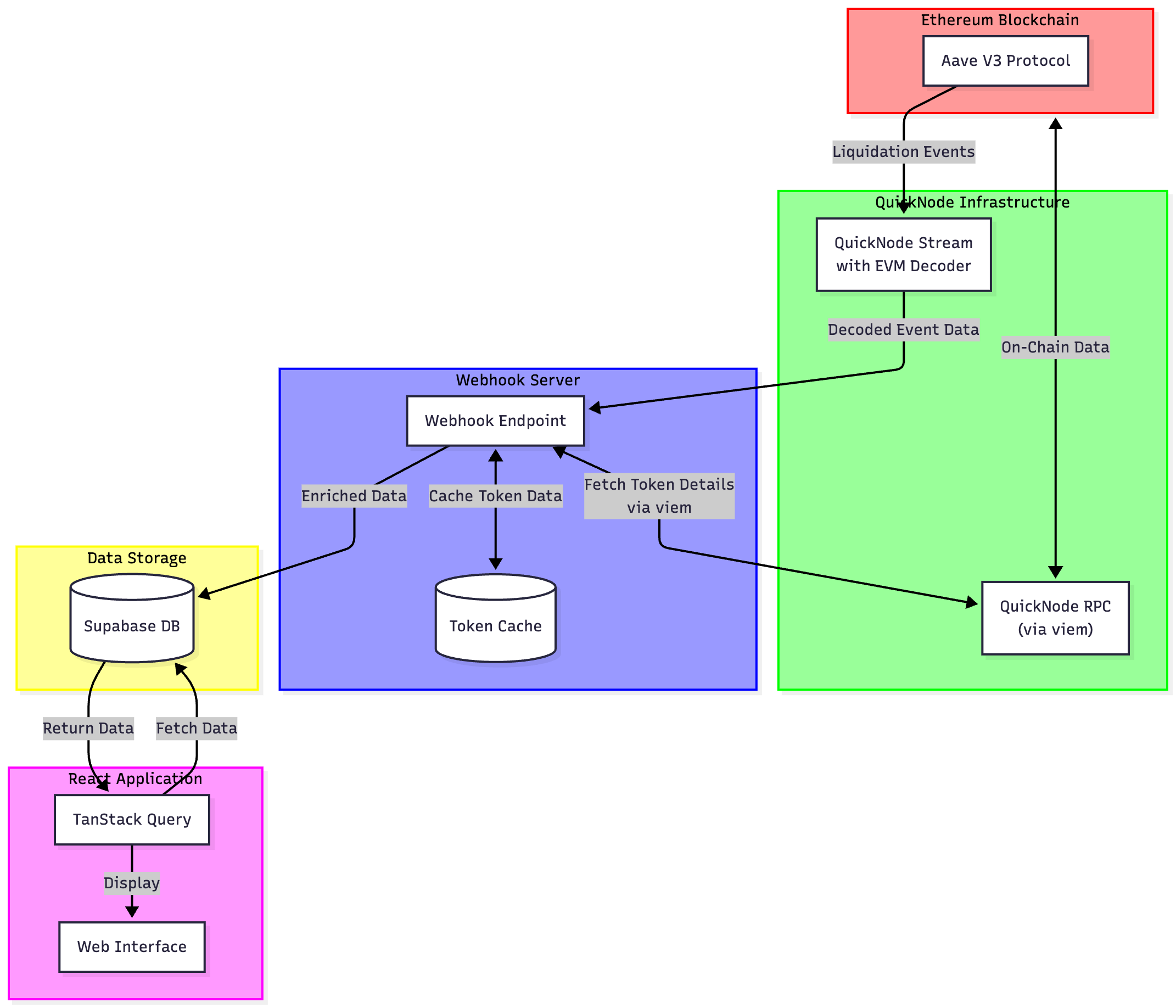
The architecture demonstrates how the system leverages Quicknode's infrastructure to process blockchain data efficiently:
- Quicknode Stream monitors Aave V3 contract events
- Events are sent to webhook server for processing
- Data is enriched with token and price information
- Processed data is stored in Supabase
- Frontend fetches and displays real-time data
Data Collection & Processing
Quicknode Streams
Quicknode Streams provide real-time blockchain data without running a node:
- Monitors Aave V3 contracts for liquidation events
- Filters and delivers only relevant events
- Ensures reliable data delivery with retry mechanisms
- Zero infrastructure maintenance required
Webhook Server
We are using a webhook server to receive and validate incoming streams data:
Additionally, we enrich streams data by providing the following data points:
- Token names/symbols (WETH, USDC, etc.)
- USD prices at liquidation time
- Formatted amounts (convert bigints to decimals)
Getting Started
Prerequisites
- Node.js 18+
- npm or yarn
- Free trial Quicknode account
- Free Supabase account
- Webhook server (ngrok or something similar)
Installation
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/quiknode-labs/qn-guide-examples.git
cd qn-guide-examples/sample-dapps/ethereum-aave-liquidation-tracker
- Install dependencies:
npm install
-
Create a new project and database in Supabase. Save the database password for later use.
-
Create a
.envfile and add your Supabase URL and publishable key. You can get the URL and key from the Supabase dashboard by clicking the Connect button in the project.
VITE_SUPABASE_URL=your_supabase_url
VITE_SUPABASE_PUBLISHABLE_DEFAULT_KEY=your_supabase_publishable_key
- Set up your database using the provided schema:
CREATE TABLE liquidations (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
liquidator_address character varying(42) NOT NULL,
liquidated_wallet character varying(42) NOT NULL,
collateral_asset character varying(42) NOT NULL,
collateral_asset_name character varying(100),
collateral_asset_symbol character varying(20),
collateral_asset_price numeric(20,6),
collateral_seized_amount numeric(78,18),
debt_asset character varying(42) NOT NULL,
debt_asset_name character varying(100),
debt_asset_symbol character varying(20),
debt_asset_price numeric(20,6),
debt_repaid_amount numeric(78,18),
transaction_hash character varying(66) NOT NULL,
block_number bigint NOT NULL,
receive_a_token boolean NOT NULL,
timestamp timestamp without time zone NOT NULL
);
- Start the development server:
npm run dev
Setting up Webhook Server
- Start your webhook server by running
npm run server. - In a separate terminal, run
ngrok http YOUR_PORT_NUMBER. For this project, the default value is set to3005but feel free to change this in.env. - Once the ngrok server is established, you will use your generated ngrok link (e.g.,
https://abcd.ngrok-free.app) and append/webhookendpoint which is where we listen to incoming data from Quicknode Streams.
Setting up Quicknode Streams
- Create a Quicknode account at quicknode.com
- Set up a new Stream:
- Select the chain and network (e.g., Ethereum Mainnet)
- Select the dataset as
Blocks with Receipts - Select start and end block numbers (for real-time data, keep
Stream endasDoesn't end) - Select the Modify the payload section and add the following Streams Filtering Code
- Select a test block (e.g.,
18983377) and clickRun test - Select the destination as
Webhookand add your webhook URL with/webhookendpoint added. - Optionally, you can add your Stream's security token in
.envto utilize advanced security features.
The contract addresses, test blocks, and other configurations may vary depending on the specific project and network you are working with. In this app, we use Ethereum Mainnet and the Aave V3 protocol.
You can get the full code for the Streams Filtering Function below or view it here.
View Streams Filtering Code
// Filtering function on Streams
function main(stream) {
try {
// Aave V3 LiquidationCall ABI
const aaveLiquidationAbi = `[{
"anonymous": false,
"inputs": [
{"indexed": true, "type": "address", "name": "collateralAsset"},
{"indexed": true, "type": "address", "name": "debtAsset"},
{"indexed": true, "type": "address", "name": "user"},
{"indexed": false, "type": "uint256", "name": "debtToCover"},
{"indexed": false, "type": "uint256", "name": "liquidatedCollateralAmount"},
{"indexed": false, "type": "address", "name": "liquidator"},
{"indexed": false, "type": "bool", "name": "receiveAToken"}
],
"name": "LiquidationCall",
"type": "event"
}]`;
// Pool.sol addresses for Aave V3 (lowercase)
const normalizedAddresses = ["0x87870bca3f3fd6335c3f4ce8392d69350b4fa4e2"];
// Handle both payload and stream parameter styles
const data = stream?.data ? stream.data : stream;
// Early validation - return null to skip (per Quicknode docs)
if (!data?.[0]?.block?.timestamp || !data?.[0]?.receipts?.length) {
return null;
}
const timestamp = parseInt(data[0].block.timestamp, 16);
// Decode receipts
const decodedReceipts = decodeEVMReceipts(data[0].receipts, [aaveLiquidationAbi]);
// Validate decoded receipts
if (!decodedReceipts || !Array.isArray(decodedReceipts) || decodedReceipts.length === 0) {
return null;
}
// Filter for liquidation events
const filteredLogs = decodedReceipts
.filter(r => r?.decodedLogs?.length > 0)
.flatMap(r => r.decodedLogs)
.filter(log =>
log?.name === "LiquidationCall" &&
log?.address &&
normalizedAddresses.includes(log.address.toLowerCase())
);
// Return data if found, null otherwise (per Quicknode docs)
return filteredLogs?.length > 0
? { timestamp, filteredLogs }
: null;
} catch (e) {
// Return null to skip on error (per Quicknode docs)
return null;
}
}
Quicknode Setup
- Log in to your Quicknode dashboard or create your free trial account.
- Create a new Endpoint for your chain and network (e.g., Ethereum Mainnet).
- Copy the RPC URL and paste it into the
QUICKNODE_RPC_URLvariable in the.envfile.
Database Setup
- Log in to your Supabase dashboard.
- Navigate to your project and click the Connect button.
- Under Connection info, click App Frameworks and set Framework to React and Using Vite framework.
- Copy
VITE_SUPABASE_URLandVITE_SUPABASE_PUBLISHABLE_DEFAULT_KEYto.env.
Setting up PostgreSQL Functions
To fetch the data from the database, you can use the following PostgreSQL queries to create some functions. These functions are used in the frontend to display the data.
View PostgreSQL Functions Code
-- get_asset_distributions
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_asset_distributions(time_range text)
RETURNS json AS $$
DECLARE
interval_start timestamp;
BEGIN
interval_start := CASE time_range
WHEN '24h' THEN NOW() - INTERVAL '24 hours'
WHEN '7d' THEN NOW() - INTERVAL '7 days'
WHEN '30d' THEN NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days'
WHEN '365d' THEN NOW() - INTERVAL '365 days'
ELSE NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days'
END;
RETURN json_build_object(
'topCollateralAssets', (
SELECT json_agg(row_to_json(t))
FROM (
SELECT
collateral_asset_symbol as symbol,
COUNT(*) as count,
SUM(collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) as totalValueUSD,
SUM((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)) as totalProfitUSD,
(COUNT(*)::float / (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM liquidations WHERE timestamp >= interval_start)::float * 100) as percentageOfTotal
FROM liquidations
WHERE timestamp >= interval_start
GROUP BY collateral_asset_symbol
ORDER BY count DESC
LIMIT 5
) t
),
'topDebtAssets', (
SELECT json_agg(row_to_json(t))
FROM (
SELECT
debt_asset_symbol as symbol,
COUNT(*) as count,
SUM(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price) as totalValueUSD,
SUM((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)) as totalProfitUSD,
(COUNT(*)::float / (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM liquidations WHERE timestamp >= interval_start)::float * 100) as percentageOfTotal
FROM liquidations
WHERE timestamp >= interval_start
GROUP BY debt_asset_symbol
ORDER BY count DESC
LIMIT 5
) t
)
);
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
-- get_metrics_overview
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_metrics_overview()
RETURNS json AS $$
BEGIN
RETURN json_build_object(
'total24h', (
SELECT json_build_object(
'count', COUNT(*),
'valueUSD', COALESCE(SUM(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price), 0),
'profitUSD', COALESCE(SUM((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)), 0)
)
FROM liquidations
WHERE timestamp >= NOW() - INTERVAL '24 hours'
),
'total7d', (
SELECT json_build_object(
'count', COUNT(*),
'valueUSD', COALESCE(SUM(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price), 0),
'profitUSD', COALESCE(SUM((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)), 0)
)
FROM liquidations
WHERE timestamp >= NOW() - INTERVAL '7 days'
),
'total30d', (
SELECT json_build_object(
'count', COUNT(*),
'valueUSD', COALESCE(SUM(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price), 0),
'profitUSD', COALESCE(SUM((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)), 0)
)
FROM liquidations
WHERE timestamp >= NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days'
),
'total365d', (
SELECT json_build_object(
'count', COUNT(*),
'valueUSD', COALESCE(SUM(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price), 0),
'profitUSD', COALESCE(SUM((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)), 0)
)
FROM liquidations
WHERE timestamp >= NOW() - INTERVAL '365 days'
),
'topLiquidators', (
SELECT json_agg(row_to_json(t))
FROM (
SELECT
liquidator_address as address,
COUNT(*) as count,
SUM(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price) as totalValueUSD,
AVG(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price) as avgLiquidationUSD,
SUM((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)) as totalProfitUSD,
AVG((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)) as avgProfitUSD
FROM liquidations
GROUP BY liquidator_address
ORDER BY totalProfitUSD DESC
LIMIT 5
) t
),
'topLiquidatedUsers', (
SELECT json_agg(row_to_json(t))
FROM (
SELECT
liquidated_wallet as address,
COUNT(*) as count,
SUM(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price) as totalValueUSD,
AVG(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price) as avgLiquidationUSD,
SUM((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)) as totalLossUSD,
AVG((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)) as avgLossUSD
FROM liquidations
GROUP BY liquidated_wallet
ORDER BY count DESC
LIMIT 5
) t
),
'largestLiquidations', (
SELECT json_agg(row_to_json(t))
FROM (
SELECT
transaction_hash as txHash,
timestamp,
debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price as valueUSD,
(collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price) as profitUSD,
collateral_asset_symbol as collateralAsset,
debt_asset_symbol as debtAsset,
liquidator_address as liquidator,
liquidated_wallet as liquidatedUser
FROM liquidations
ORDER BY debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price DESC
LIMIT 5
) t
),
'mostProfitableLiquidations', (
SELECT json_agg(row_to_json(t))
FROM (
SELECT
transaction_hash as txHash,
timestamp,
debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price as valueUSD,
(collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price) as profitUSD,
collateral_asset_symbol as collateralAsset,
debt_asset_symbol as debtAsset,
liquidator_address as liquidator,
liquidated_wallet as liquidatedUser
FROM liquidations
ORDER BY ((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)) DESC
LIMIT 5
) t
)
);
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
-- get_liquidation_trends
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_liquidation_trends(time_range text)
RETURNS json AS $$
DECLARE
interval_start timestamp;
grouping_interval text;
BEGIN
SELECT
CASE time_range
WHEN '24h' THEN NOW() - INTERVAL '24 hours'
WHEN '7d' THEN NOW() - INTERVAL '7 days'
WHEN '30d' THEN NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days'
WHEN '365d' THEN NOW() - INTERVAL '365 days'
ELSE NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days'
END,
CASE time_range
WHEN '24h' THEN 'hour'
WHEN '7d' THEN 'day'
WHEN '30d' THEN 'day'
WHEN '365d' THEN 'month'
ELSE 'day'
END
INTO interval_start, grouping_interval;
RETURN (
SELECT json_agg(row_to_json(t))
FROM (
SELECT
date_trunc(grouping_interval, timestamp) as date,
COUNT(*) as count,
COALESCE(SUM(debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price), 0) as totalValueUSD,
COALESCE(SUM((collateral_seized_amount * collateral_asset_price) - (debt_repaid_amount * debt_asset_price)), 0) as totalProfitUSD
FROM liquidations
WHERE timestamp >= interval_start
GROUP BY date_trunc(grouping_interval, timestamp)
ORDER BY date_trunc(grouping_interval, timestamp)
) t
);
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
Setting up PostgreSQL Indexes
For better query performance, we can create indexes on the liquidations table. Here's an example of how to create the necessary indexes:
CREATE INDEX idx_debt_asset ON liquidations(debt_asset_symbol text_ops);
CREATE INDEX idx_timestamp ON liquidations(timestamp timestamp_ops);
CREATE INDEX idx_liquidator_address ON liquidations(liquidator_address text_ops);
CREATE INDEX idx_liquidated_wallet ON liquidations(liquidated_wallet text_ops);
CREATE INDEX idx_collateral_asset ON liquidations(collateral_asset_symbol text_ops);
CREATE INDEX idx_liquidations_assets ON liquidations(collateral_asset_symbol text_ops,debt_asset_symbol text_ops);
Development
Project Structure
src/
├── components/ # Reusable UI components
├── hooks/ # Custom React hooks
├── lib/
│ ├── security.ts # Validating incoming Streams data
│ ├── server.ts # Our webhook server
│ ├── supabase-backend.ts # Supabase keys for backend operations
│ ├── supabase-frontend.ts # Supabase keys for frontend operations
│ ├── transform.ts # Data transformation of incoming Streams data
│ └── utils.ts # General utility functions
└── types/ # TypeScript type definitions
Available Scripts
npm run dev: Start development servernpm run build: Build for productionnpm run server: Start webhook servernpm run lint: Run ESLint
Possible Future Features
Advanced Features
- Whale wallet tracking
- Custom alert thresholds
- Portfolio risk assessment
- Integration with other DeFi protocols
- Real-time notifications for:
- Large liquidations
- Specific assets
- Price threshold alerts
Technical Enhancements
- WebSocket support for real-time updates
- Multiple network support (Polygon, Arbitrum, etc.)
- Advanced data visualization options
- Mobile app version
- API access for developers
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch:git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature
- Commit your changes:git commit -m "Add amazing feature"
- Push your branch:git push origin feature/amazing-feature
- Open a Pull Request.