3 min read
Overview
If you’re building a Quicknode add-on that makes use of JSON-RPC methods, then this guide is for you. In it, we’ll cover how Quicknode creates and shares the identifiers used for billing, as well as how we use these IDs during the request/response cycle for a given RPC method from your add-on.
Understanding Quicknode ID’s
We create a single ID for each customer on Quicknode, which takes the form of a Sha256 hash. During the add-on provisioning process, we share this ID with you, so you can store which customers should get access to which services you provide. It comes over in the payload for provisioning, updating, and de-provisioning, as discussed in the Provisioning APIs article.
The ID is unique to a customer, who may have several installs of your add-on, which are billed on an account basis.
Request/Response Lifecycle
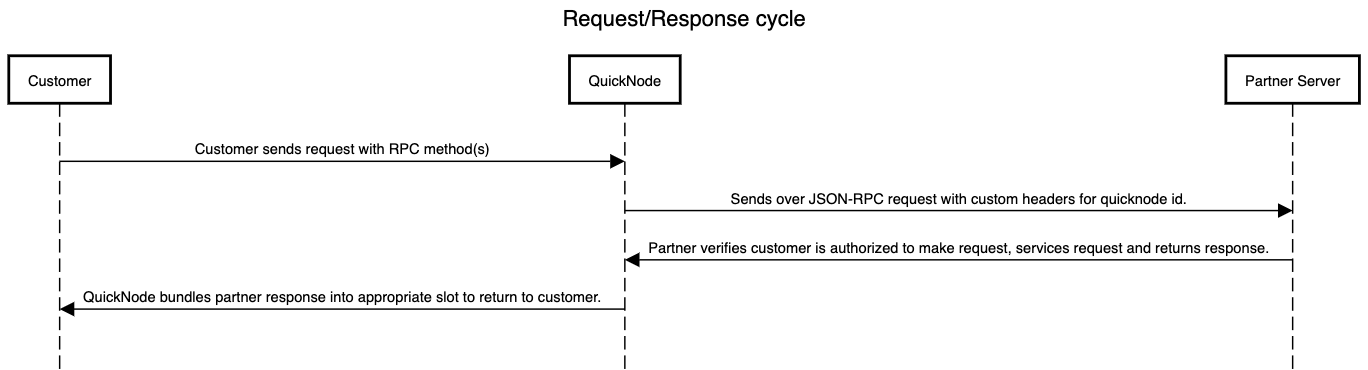
We’ve created a diagram for your convenience which is below, but when a request comes into Quicknodes infrastructure, this is how we handle it for RPC add-ons at a high level:
- Customer sends request with RPC method(s).
- Quicknode sends over JSON-RPC request with custom headers for quicknode id.
- Partner verifies customer is authorized to make request, services request and returns response.
- Quicknode bundles partner response into appropriate slot to return to customer.
On your side as a partner, you should focus on confirming that the add-on is still active for the customer and then servicing the response as quickly as possible. Quicknode will enforce the add-on plan's Request Per Seconds Limit (RPS Limit) and Monthly Requests Limit for customers, if you have set them up.
| Condition set by you | Enforcement by Quicknode |
|---|---|
| Both RPS and Monthly Limits are set | Enforces both limits |
| Only RPS Limit is set | Enforces only the RPS Limit |
| Only Monthly Requests Limit is set | Enforces only the Monthly Requests Limit |
| No limits are set | No enforcement |
With that in mind, we’re going to look specifically at the custom headers we send.
Headers
When Quicknode forwards a request to your upstream service, you should always inspect the following headers:
X-QUICKNODE-ID: 969d539bf782b561aeff148b2a94cc3705720f3d38e147e475912e53b4e96a85
This X-QUICKNODE-ID value uniquely identifies the paying customer. You should have already stored this ID in your database during the provisioning process, if your add-on has the provisioning API authorization method.
Note: Requests containing the
X-QN-TESTINGheader come from the Quicknode team or automated testing tools.
Additional headers you can expect include:
X-INSTANCE-ID– Identifies the specific endpoint instance.X-QN-CHAIN– Indicates the blockchain network name (e.g.,ethereum). See the full list of supported chains here.X-QN-NETWORK– Specifies the network environment (e.g.,mainnet). The complete list of supported networks is available here.
Be sure to log and validate these headers appropriately as they help you associate requests with the correct customer and environment.
Conclusion
That’s it! If you have any questions, please reach out to us.
Subscribe to our newsletter for more articles and guides on Web3 and blockchain. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to join our Discord server or provide feedback using the form below. Stay up to date with the latest by following us on Twitter (@Quicknode) and our Telegram announcement channel.
We ❤️ Feedback!
Let us know if you have any feedback or requests for new topics. We'd love to hear from you.