31 min read
Overview
Solana transaction fees are paid in SOL, which means users need some SOL in their wallet to complete transactions. This can create friction for apps when users hold USDC or other SPL tokens but don’t have SOL available. Kora removes this barrier by allowing transaction and priority fees (sometimes called “gas”) to be paid in supported SPL tokens, or by sponsoring fees entirely so users pay nothing.
Behind the scenes, Kora acts as a fee payer that validates transactions against your security rules before signing. You maintain complete control over allowed programs, tokens, and spending limits.
This guide walks you through setting up a local Kora server, configuring validation rules, and building TypeScript unit tests that create a genuinely gasless user experience.
What You Will Do
- Install and configure a local Kora RPC server
- Define validation rules for programs, tokens, and spending limits
- Initialize a test environment with local tokens and Associated Token Accounts (ATAs)
- Build a TypeScript client that creates gasless transactions
- Test complete fee-payment flows using SPL tokens instead of SOL
What You Will Need
This guide assumes basic familiarity with Solana transactions, SPL tokens, Associated Token Accounts (ATAs), and TypeScript.
For a quick recap before you begin, these guides can help:
- Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Solana Transactions
- Get All Token Accounts Held by a Solana Wallet
- Five Ways to Find the Associated Token Address for a Solana Wallet and Mint
- How to Send Transactions with Solana Kit
This guide will use the following packages and libraries:
| Dependency | Version |
|---|---|
| Node | 22+ |
| Solana CLI | 3.0.6+ |
| Kora CLI | 2.0.1 |
| @solana/kit | 5.5.1 |
| @solana/kora | 0.1.0 |
| @solana/codecs | 6.0.1 |
| @solana-program/system | 0.10.0 |
| @solana-program/token | 0.9.0 |
| tsx | 4.7.0 |
Kora's Architecture
Kora consists of 3 main components:
- Your client (dApp/wallet) that builds the unsigned transaction
- The Kora server that validates it against your rules and signs as the fee payer
- A Solana RPC endpoint that broadcasts the signed transaction to the network
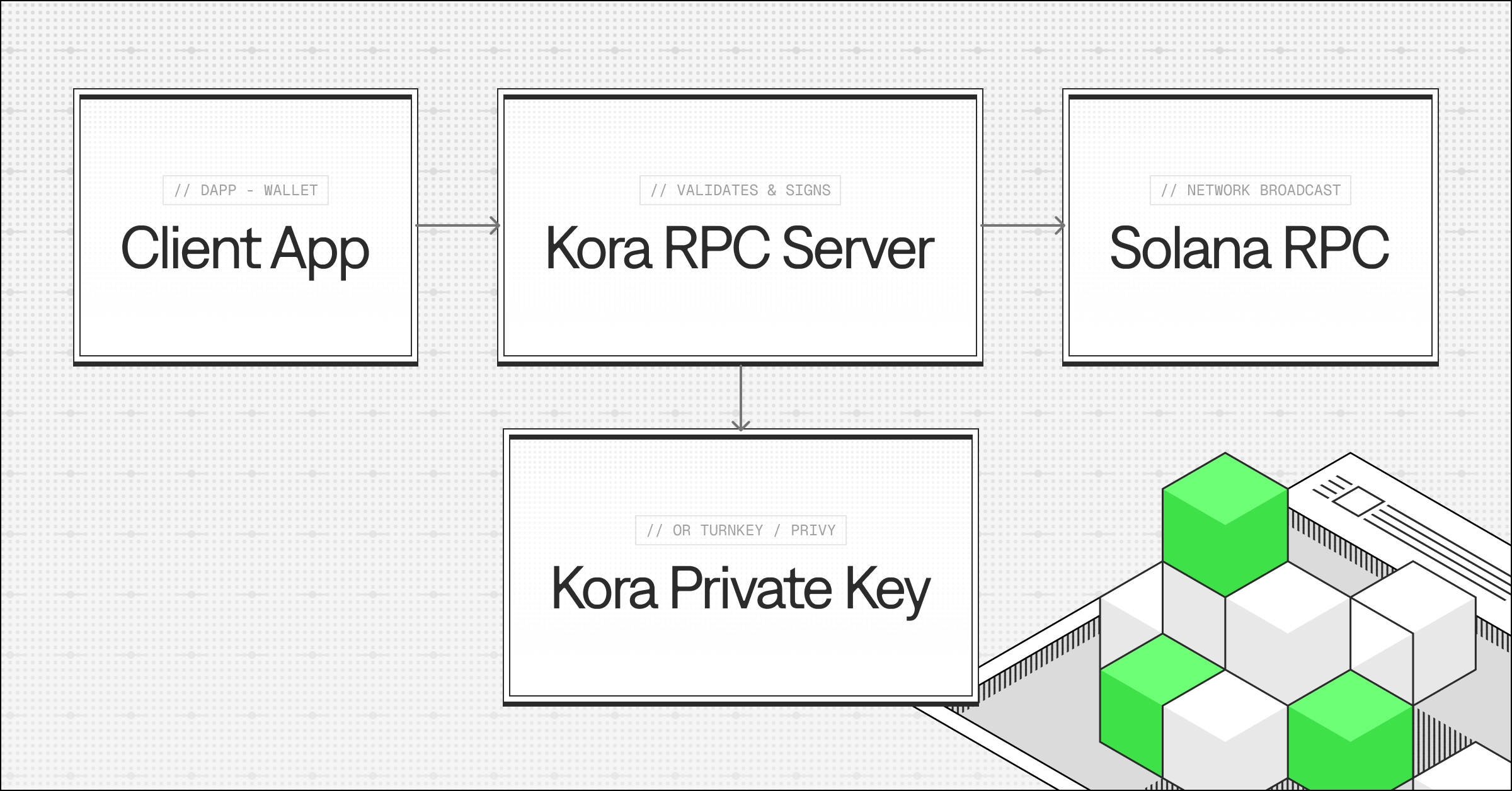
This validation-first approach ensures Kora only signs transactions that comply with your security rules. You specify exactly which programs can be called, set spending limits per transaction and account, and define which tokens are acceptable for payment. You can even block specific accounts.
The complete transaction flow works like this:
- Your client constructs a transaction with Kora's address as the fee payer
- Client sends the unsigned transaction to Kora RPC server
- Kora validates the transaction against configured rules
- If valid, Kora signs the transaction with its fee payer keypair
- Kora either returns the signed transaction to your client or submits it directly to Solana
This architecture creates a clear separation of concerns: your client manages user interaction and transaction construction, Kora handles validation and signing, and Solana executes the transaction on-chain. The result is a system that enables gasless experiences without sacrificing security or control over spending.
Install Kora
Kora is distributed as a Rust CLI tool. Install it globally using Cargo:
cargo install kora-cli
After installation completes, verify it's available:
kora --version
The kora binary provides commands for running the RPC server, initializing payment accounts, and managing configuration.
Set Up Project
You'll build a complete gasless transaction implementation from scratch, creating all the necessary files and configuration. By the end of this guide, you'll have a working example that demonstrates how to integrate Kora into your applications.
Create a new project directory:
mkdir kora-gasless-demo
cd kora-gasless-demo
Initialize a Node.js project and install dependencies:
npm init -y
npm install @solana/kit @solana/kora @solana-program/token @solana-program/system @solana/codecs
npm install --save-dev typescript tsx @types/node
Add package.json type and scripts:
npm pkg set type="module"
npm pkg set scripts.env-setup="tsx --env-file=.env setup.ts"
npm pkg set scripts.test="tsx --env-file=.env --test test/gasless-transfer.test.ts"
For setup, config, and end-to-end tests, we'll create these files:
- .env: Environment configuration for connecting to Kora and Solana
- setup.ts: Script that creates test tokens, initializes ATAs, and funds accounts
- kora.toml: Kora server configuration with validation rules
- signers.toml: Kora Signer configuration for the fee payer
- test/gasless-transfer.test.ts: Complete test suite demonstrating Kora integration
Configure Kora
Before running the setup script, you need to create Kora's configuration files. These define the security rules Kora enforces and how it manages signing keys.
Create kora.toml
Create a file named kora.toml in your project root. This file is the heart of Kora's security model. It defines exactly what Kora will allow to be signed.
# Kora RPC Server Configuration
[kora]
rate_limit = 100 # Global rate limit (requests per second) across all clients
[kora.auth]
# Authentication disabled for local testing
[kora.cache]
enabled = false
default_ttl = 300
account_ttl = 60
[kora.enabled_methods]
liveness = false
estimate_transaction_fee = true
get_supported_tokens = true
sign_transaction = true
sign_and_send_transaction = true
transfer_transaction = true
get_blockhash = true
get_config = true
get_payer_signer = true
[validation]
max_allowed_lamports = 1000000000 # 1 SOL
max_signatures = 10
price_source = "Mock"
allow_durable_transactions = false
allowed_programs = [
"11111111111111111111111111111111", # System Program
"TokenkegQfeZyiNwAJbNbGKPFXCWuBvf9Ss623VQ5DA", # Token Program
"ATokenGPvbdGVxr1b2hvZbsiqW5xWH25efTNsLJA8knL", # Associated Token Program
]
allowed_tokens = ["YOUR_USDC_MINT_ADDRESS"]
allowed_spl_paid_tokens = ["YOUR_USDC_MINT_ADDRESS"]
disallowed_accounts = []
[validation.fee_payer_policy]
[validation.fee_payer_policy.system]
allow_transfer = true
allow_assign = true
allow_create_account = true
allow_allocate = true
[validation.fee_payer_policy.system.nonce]
allow_initialize = true
allow_advance = true
allow_authorize = true
allow_withdraw = true
[validation.fee_payer_policy.spl_token]
allow_transfer = true
allow_burn = true
allow_close_account = true
allow_approve = true
allow_revoke = true
allow_set_authority = true
allow_mint_to = true
allow_initialize_mint = true
allow_initialize_account = true
allow_initialize_multisig = true
allow_freeze_account = true
allow_thaw_account = true
[validation.fee_payer_policy.token_2022]
allow_transfer = true
allow_burn = true
allow_close_account = true
allow_approve = true
allow_revoke = true
allow_set_authority = true
allow_mint_to = true
allow_initialize_mint = true
allow_initialize_account = true
allow_initialize_multisig = true
allow_freeze_account = true
allow_thaw_account = true
[validation.price]
type = "margin"
margin = 0.1 # 10% margin
[validation.token2022]
blocked_mint_extensions = []
blocked_account_extensions = []
[kora.usage_limit]
enabled = false
cache_url = "redis://localhost:6379"
max_transactions = 2
fallback_if_unavailable = false
Validation Rules control which transactions Kora will sign:
max_allowed_lamports sets the maximum fee per transaction. This protects against expensive transactions or bugs that could drain your fee payer account.
allowed_programs is an allowlist of program IDs that transactions can invoke. Kora rejects any transaction attempting to call programs not in this list. Start with System Program, Token Program, and Associated Token Program, then add your application's programs as needed.
allowed_tokens specifies which token mints can be transferred in transactions. You'll add your test USDC mint address here after running the setup script.
allowed_spl_paid_tokens is a subset of allowed_tokens that Kora accepts as fee payment. Typically includes stablecoins or your native token. You'll add your test USDC mint address here.
price_source = "Mock" uses fixed conversion rates defined in your config. Ideal for local development and testing. For production deployments you would use price_source = "Jupiter".
margin = 0.1 adds a 10% buffer above the actual cost to protect against price fluctuations between fee estimation and transaction execution.
Fee Payer Policies define which Solana operations Kora allows across System Program, SPL Token, and Token Extensions instructions. These granular controls let you permit specific instruction types (transfers, mints, burns, etc.) while blocking others.
Create signers.toml
Create a file named signers.toml in your project root. This configures how Kora manages its signing keys:
# Kora Signers Configuration
[signer_pool]
strategy = "round_robin"
[[signers]]
name = "fee_payer"
type = "memory"
private_key_env = "KORA_PRIVATE_KEY"
weight = 1
This configuration uses a memory-based signer that loads the keypair from the KORA_PRIVATE_KEY environment variable. The signer pool uses a round_robin strategy, which distributes transactions evenly across multiple signers (though we only have one signer in this example).
For production, you would replace the memory signer with a secure key management service like Turnkey, Vault, or Privy to keep private keys in hardware security modules (HSMs) and provide signing through secure APIs.
Generate Required Keypairs
Start a local Solana test validator in a separate terminal:
solana-test-validator
Generate the four required keypairs:
solana-keygen new --outfile kora-fee-payer.json --no-bip39-passphrase
solana-keygen new --outfile user-keypair.json --no-bip39-passphrase
solana-keygen new --outfile recipient-keypair.json --no-bip39-passphrase
solana-keygen new --outfile mint-authority-keypair.json --no-bip39-passphrase
Fund these accounts with SOL from your local validator:
solana airdrop 1 -k kora-fee-payer.json
solana airdrop 1 -k user-keypair.json
solana airdrop 1 -k recipient-keypair.json
solana airdrop 1 -k mint-authority-keypair.json
Configure Environment Variables
Create a .env file to store your environment variables:
# Kora fee payer private key (path to keypair file or base58 string)
KORA_PRIVATE_KEY=kora-fee-payer.json
# USDC mint address (generated by setup script)
USDC_MINT_ADDRESS=MINT_ADDRESS_FROM_SETUP
# RPC URLs
SOLANA_RPC_URL=http://localhost:8899
SOLANA_WS_URL=ws://localhost:8900
KORA_RPC_URL=http://localhost:8080
Create Setup Script
Create a file named setup.ts in your project root. This script automates the entire test environment setup by loading the four keypairs you created earlier, generating a new SPL token to represent USDC, and initializing all necessary Associated Token Accounts.
It mints 1,000 USDC to the user's account for testing, creates Kora's ATA for receiving fee payments, and sets up the recipient's ATA for receiving transfers. When complete, the script outputs the USDC mint address you'll need to add to your configuration files.
import { readFile } from 'fs/promises';
import {
createKeyPairSignerFromBytes,
generateKeyPairSigner,
createSolanaRpc,
createSolanaRpcSubscriptions,
pipe,
createTransactionMessage,
setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner,
setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash,
appendTransactionMessageInstruction,
signTransactionMessageWithSigners,
sendAndConfirmTransactionFactory
} from '@solana/kit';
import {
getInitializeMint2Instruction,
getMintToInstruction,
TOKEN_PROGRAM_ADDRESS
} from '@solana-program/token';
import { getCreateAccountInstruction } from '@solana-program/system';
import { getCreateAssociatedTokenInstructionAsync } from '@solana-program/token';
const RPC = process.env.SOLANA_RPC_URL || 'http://localhost:8899';
const WS = process.env.SOLANA_WS_URL || 'ws://localhost:8900';
async function main() {
console.log('\n🚀 Setup\n');
const rpc = createSolanaRpc(RPC);
const rpcSubs = createSolanaRpcSubscriptions(WS);
const sendAndConfirm = sendAndConfirmTransactionFactory({ rpc, rpcSubscriptions: rpcSubs });
// Load keypairs
console.log('1️⃣ Loading keypairs...');
const loadKey = async (f: string) => createKeyPairSignerFromBytes(
new Uint8Array(JSON.parse(await readFile(f, 'utf-8')))
);
const [kora, user, recipient, mintAuth] = await Promise.all([
loadKey('kora-fee-payer.json'),
loadKey('user-keypair.json'),
loadKey('recipient-keypair.json'),
loadKey('mint-authority-keypair.json')
]);
console.log(' ✅ Done');
// Create mint
console.log('\n2️⃣ Creating USDC mint...');
const mint = await generateKeyPairSigner();
const latestBlockhash = await rpc.getLatestBlockhash().send();
const rentExempt = await rpc.getMinimumBalanceForRentExemption(BigInt(82)).send();
const createMintTx = pipe(
createTransactionMessage({ version: 0 }),
tx => setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner(mintAuth, tx),
tx => setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash(latestBlockhash.value, tx),
tx => appendTransactionMessageInstruction(
getCreateAccountInstruction({
payer: mintAuth,
newAccount: mint,
lamports: rentExempt,
space: 82n,
programAddress: TOKEN_PROGRAM_ADDRESS
}),
tx
),
tx => appendTransactionMessageInstruction(
getInitializeMint2Instruction({
mint: mint.address,
decimals: 6,
mintAuthority: mintAuth.address
}),
tx
)
);
const signedMintTx = await signTransactionMessageWithSigners(createMintTx);
await sendAndConfirm(signedMintTx, { commitment: 'confirmed' });
console.log(` ✅ ${mint.address}`);
// Mint to user (auto-creates ATA)
console.log('\n3️⃣ Minting 1000 USDC to user...');
const createUserAtaIx = await getCreateAssociatedTokenInstructionAsync({
payer: user,
owner: user.address,
mint: mint.address
});
const userAta = createUserAtaIx.accounts[1].address;
const bh2 = await rpc.getLatestBlockhash().send();
const mintToUserTx = pipe(
createTransactionMessage({ version: 0 }),
tx => setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner(user, tx),
tx => setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash(bh2.value, tx),
tx => appendTransactionMessageInstruction(createUserAtaIx, tx),
tx => appendTransactionMessageInstruction(
getMintToInstruction({
mint: mint.address,
token: userAta,
mintAuthority: mintAuth,
amount: 1000_000000n
}),
tx
)
);
const signedUserTx = await signTransactionMessageWithSigners(mintToUserTx);
await sendAndConfirm(signedUserTx, { commitment: 'confirmed' });
console.log(' ✅ Done');
// Create Kora ATA
console.log('\n4️⃣ Creating Kora ATA...');
const createKoraAtaIx = await getCreateAssociatedTokenInstructionAsync({
payer: kora,
owner: kora.address,
mint: mint.address
});
const bh3 = await rpc.getLatestBlockhash().send();
const koraTx = pipe(
createTransactionMessage({ version: 0 }),
tx => setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner(kora, tx),
tx => setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash(bh3.value, tx),
tx => appendTransactionMessageInstruction(createKoraAtaIx, tx)
);
const signedKoraTx = await signTransactionMessageWithSigners(koraTx);
await sendAndConfirm(signedKoraTx, { commitment: 'confirmed' });
console.log(' ✅ Done');
// Create recipient ATA
console.log('\n5️⃣ Creating recipient ATA...');
const createRecipientAtaIx = await getCreateAssociatedTokenInstructionAsync({
payer: recipient,
owner: recipient.address,
mint: mint.address
});
const bh4 = await rpc.getLatestBlockhash().send();
const recipientTx = pipe(
createTransactionMessage({ version: 0 }),
tx => setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner(recipient, tx),
tx => setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash(bh4.value, tx),
tx => appendTransactionMessageInstruction(createRecipientAtaIx, tx)
);
const signedRecipientTx = await signTransactionMessageWithSigners(recipientTx);
await sendAndConfirm(signedRecipientTx, { commitment: 'confirmed' });
console.log(' ✅ Done');
// Output
console.log('\n✅ Setup complete!\n');
console.log('📋 Next steps:\n');
console.log('1. Update .env with the new USDC mint address:\n');
console.log(` USDC_MINT_ADDRESS=${mint.address}\n`);
console.log('2. Update kora.toml:\n');
console.log(` allowed_tokens = ["${mint.address}"]`);
console.log(` allowed_spl_paid_tokens = ["${mint.address}"]\n`);
console.log('3. Start Kora: kora rpc start --signers-config signers.toml\n');
console.log('4. Run tests: npm run test\n');
}
main().catch(console.error);
Run the setup script:
npm run env-setup
After you have run setup successfully, you will see the following (your USDC Mint address will be different):
🚀 Setup
1️⃣ Loading keypairs...
✅ Done
2️⃣ Creating USDC mint...
✅ GK2oJXymkRtjp417b4MTMqouxxApBXbZn6Jmw2rZWxDk
3️⃣ Minting 1000 USDC to user...
✅ Done
4️⃣ Creating Kora ATA...
✅ Done
5️⃣ Creating recipient ATA...
✅ Done
✅ Setup complete!
📋 Next steps:
1. Update .env with the new USDC mint address:
USDC_MINT_ADDRESS=GK2oJXymkRtjp417b4MTMqouxxApBXbZn6Jmw2rZWxDk
2. Update kora.toml:
allowed_tokens = ["GK2oJXymkRtjp417b4MTMqouxxApBXbZn6Jmw2rZWxDk"]
allowed_spl_paid_tokens = ["GK2oJXymkRtjp417b4MTMqouxxApBXbZn6Jmw2rZWxDk"]
3. Start Kora: kora rpc start --signers-config signers.toml
4. Run tests: npm run test
The script will output the address for your USDC mint. You'll need it for the Kora configuration files in the next steps.
Also be sure to update .env with your USDC mint address.
Update Kora Configuration
Open kora.toml and update the token allowlists with your mint address:
allowed_tokens = ["MINT_ADDRESS_FROM_SETUP"]
allowed_spl_paid_tokens = ["MINT_ADDRESS_FROM_SETUP"]
Replace MINT_ADDRESS_FROM_SETUP with your mint address. This tells Kora to accept your test USDC as both a transferable token and a fee payment token.
Start the Kora Server
With configuration complete and payment accounts initialized, start the Kora RPC server in a new terminal:
kora rpc start --signers-config signers.toml
The server reads kora.toml from the current directory. Once it starts, you'll see output indicating it's listening on http://localhost:8080. The server is now ready to accept JSON-RPC requests, validate transactions, and sign approved transactions as a fee payer.
Leave this terminal running with the Kora server active while you create and run the tests.
Create the Test Suite
Now you'll create a comprehensive test suite that demonstrates all of Kora's functionality. Create a directory for tests:
mkdir test
touch test/gasless-transfer.test.ts
We'll build this file section by section to understand how each part works.
Imports and Configuration
This section sets up the test infrastructure by importing dependencies and defining configuration constants. The code imports testing utilities, transaction building functions, and the Kora client. It then defines constants for RPC URLs, token mint addresses, and program IDs that will be used throughout the tests.
import { describe, it, before } from 'node:test';
import assert from 'node:assert';
import { readFile } from 'fs/promises';
import {
createKeyPairSignerFromBytes,
createSolanaRpc,
getAddressEncoder,
getProgramDerivedAddress,
address,
getBase64EncodedWireTransaction,
partiallySignTransactionMessageWithSigners,
partiallySignTransaction,
createNoopSigner,
setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner,
createTransactionMessage,
setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash,
appendTransactionMessageInstruction,
pipe,
type Address,
type KeyPairSigner
} from '@solana/kit';
import { KoraClient } from '@solana/kora';
import { getBase58Decoder } from "@solana/codecs";
const USDC_MINT_ADDRESS = process.env.USDC_MINT_ADDRESS!;
const SOLANA_RPC_URL = process.env.SOLANA_RPC_URL || 'http://localhost:8899';
const KORA_RPC_URL = process.env.KORA_RPC_URL || 'http://localhost:8080';
const LAMPORTS_PER_SOL = 1_000_000_000;
const USDC_DECIMALS = 6;
const TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID = address('TokenkegQfeZyiNwAJbNbGKPFXCWuBvf9Ss623VQ5DA');
const ASSOCIATED_TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID = address('ATokenGPvbdGVxr1b2hvZbsiqW5xWH25efTNsLJA8knL');
interface TestEnvironment {
rpc: any;
koraClient: KoraClient;
userKeypair: KeyPairSigner;
recipientKeypair: KeyPairSigner;
usdcMint: Address;
}
let env: TestEnvironment;
Helper Functions
This section defines utility functions that will be used throughout the test suite to get keypairs from files, compute Associated Token Account (ATA) addresses, and get SOL and token balances for a wallet.
// Loads a keypair from a JSON file
async function loadKeypair(filepath: string): Promise<KeyPairSigner> {
const bytes = JSON.parse(await readFile(filepath, 'utf-8'));
return await createKeyPairSignerFromBytes(new Uint8Array(bytes));
}
// Derives the ATA address for a given mint and owner
async function deriveAssociatedTokenAddress(mint: Address, owner: Address): Promise<Address> {
const addressEncoder = getAddressEncoder();
const [ata] = await getProgramDerivedAddress({
programAddress: ASSOCIATED_TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID,
seeds: [
addressEncoder.encode(owner),
addressEncoder.encode(TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID),
addressEncoder.encode(mint)
]
});
return ata;
}
// Queries both SOL and USDC balances for a wallet (for testing)
async function getBalances(rpc: any, walletAddress: Address, usdcMint: Address) {
const solBalanceResponse = await rpc.getBalance(walletAddress).send();
const solBalance = Number(solBalanceResponse.value) / LAMPORTS_PER_SOL;
const usdcATA = await deriveAssociatedTokenAddress(usdcMint, walletAddress);
try {
const accountInfo = await rpc.getAccountInfo(usdcATA, { encoding: 'jsonParsed' }).send();
let usdcBalance = 0;
if (accountInfo.value) {
const parsedData = accountInfo.value.data as any;
const amount = parsedData.parsed?.info?.tokenAmount?.amount;
usdcBalance = amount ? Number(amount) / (10 ** USDC_DECIMALS) : 0;
}
return { sol: solBalance, usdc: usdcBalance };
} catch {
return { sol: solBalance, usdc: 0 };
}
}
Gasless Transfer Function
This section implements the core gasless transfer function that demonstrates the complete Kora integration workflow where the user pays the transaction fee in USDC instead of SOL.
The gasless transaction begins by calling transferTransaction to construct the transfer instructions and set up the transaction structure with Kora's address as the fee payer. The response includes all the instructions needed for the transfer along with the blockhash and signer information.
Next, we call getPaymentInstruction to calculate how much USDC the user needs to pay to cover the transaction fee, using the configured price source.
We then combine the transfer instructions from transferTransaction with the payment instruction from getPaymentInstruction into a single transaction using a noop signer as a placeholder for Kora's signature, since Kora will add its actual signature in the next step.
The user signs the transaction with their keypair, authorizing both the token transfer to the recipient and the USDC payment to Kora. The transaction now has the user's signature but still needs Kora's signature as the fee payer before it can be submitted to Solana.
Finally, we send the partially-signed transaction to Kora by calling signAndSendTransaction. Kora validates the transaction against its configuration rules, adds its signature as the fee payer, and broadcasts the fully-signed transaction to Solana. The function extracts the transaction signature from the response, which can be used to track the transaction on Solana explorers or implement monitoring and retry logic.
async function executeGaslessTransfer({
rpc,
koraClient,
userKeyPair,
recipientAddress,
usdcMint,
amount
}: {
koraClient: KoraClient;
userKeyPair: KeyPairSigner;
recipientAddress: Address;
usdcMint: Address;
amount: number;
}) {
console.log(`📝 Constructing transfer: ${amount} USDC`);
// Step 1: Use Kora's transferTransaction to build the gasless transfer
// This method automatically handles:
// - Building the transfer instruction
// - Adding payment instruction for fee in USDC
// - Getting blockhash
// - Setting up the transaction structure with Kora as fee payer
console.log('🔧 Building transaction with Kora');
const transferResponse = await koraClient.transferTransaction({
amount: amount * Math.pow(10, USDC_DECIMALS),
token: usdcMint,
source: userKeyPair.address, // Source wallet (not token account)
destination: recipientAddress // Destination wallet (not token account)
});
// Step 2: Get payment instruction from Kora
// transferTransaction() doesn't include payment, so we must add it manually
console.log('💵 Getting payment instruction from Kora');
const paymentResponse = await koraClient.getPaymentInstruction({
transaction: transferResponse.transaction,
fee_token: usdcMint,
source_wallet: userKeyPair.address
});
const feeInSol = Number(paymentResponse.payment_amount) / Math.pow(10, USDC_DECIMALS) / 140;
const feeInUsdc = Number(paymentResponse.payment_amount) / Math.pow(10, USDC_DECIMALS);
console.log(` Fee: ${feeInSol.toFixed(9)} SOL (~${feeInUsdc.toFixed(4)} USDC)`);
// Step 3: Build complete transaction with transfer + payment instructions
console.log('✍️ Building transaction with user signature');
// Get fresh blockhash with lastValidBlockHeight
const latestBlockhash = await rpc.getLatestBlockhash().send();
// Add transfer instructions from Kora + payment instruction
const allInstructions = [
...transferResponse.instructions,
paymentResponse.payment_instruction
];
// Build complete transaction with noop signer as fee payer placeholder
// (Kora will be the actual fee payer)
const noopSigner = createNoopSigner(address(transferResponse.signer_pubkey));
const txMessage: any = allInstructions.reduce(
(tx: any, instruction: any) => appendTransactionMessageInstruction(instruction, tx),
pipe(
createTransactionMessage({ version: 0 }),
tx => setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner(noopSigner, tx),
tx => setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash(latestBlockhash.value, tx)
)
);
// Partially sign with noop signer (placeholder)
const partiallySigned = await partiallySignTransactionMessageWithSigners(txMessage);
// User signs with their keypair (authorizes token transfer and payment)
const userSigned = await partiallySignTransaction([userKeyPair.keyPair], partiallySigned);
// Encode to base64 for sending to Kora
const signedTxBase64 = getBase64EncodedWireTransaction(userSigned);
// Step 4: Send to Kora for co-signing and broadcasting
// Kora will add its signature as fee payer AND broadcast in one step
console.log('📤 Sending to Kora for co-signing and broadcast');
const response = await koraClient.signAndSendTransaction({
transaction: signedTxBase64
});
// Extract the transaction signature from the response
// signAndSendTransaction returns the signed transaction in base64 format
// Solana transaction format: [num_signatures: 1 byte][signatures: 64 bytes each][message: rest]
const signedTxBytes = Buffer.from(response.signed_transaction, 'base64');
// First signature starts at byte 1 (after the count byte) and is 64 bytes
const signatureBytes = signedTxBytes.slice(1, 65);
// Convert signature bytes to base58 (Solana's standard signature format)
const signature = getBase58Decoder().decode(signatureBytes);
console.log(`✅ Transaction completed successfully\n`);
return {
signature,
fee: BigInt(paymentResponse.payment_amount),
feeInUsdc,
amount
};
}
Test Setup (Before Hook)
This section defines the test initialization that runs once before all tests execute to set up the shared test environment.
The setup first verifies the Solana test validator is running by calling getHealth and checks that the Kora server is running by calling getConfig, then loads the user and recipient keypairs and stores all initialized objects in the env variable that all tests can access.
// Test Setup - Runs once before all tests
before(async () => {
console.log('\n🚀 Loading test environment...\n');
const rpc = createSolanaRpc(SOLANA_RPC_URL);
// Check validator is running
try {
await rpc.getHealth().send();
console.log('✅ Connected to Solana test validator');
} catch (error) {
console.error('❌ Cannot connect to Solana validator at', SOLANA_RPC_URL);
console.error(' Start with: solana-test-validator');
throw error;
}
// Check Kora server is running
const koraClient = new KoraClient({ rpcUrl: KORA_RPC_URL });
try {
await koraClient.getConfig();
console.log('✅ Connected to Kora RPC server\n');
} catch (error) {
console.error('��❌ Cannot connect to Kora server at', KORA_RPC_URL);
console.error(' Start with: kora rpc start --signers-config signers.toml');
throw error;
}
// Load keypairs from files (created by setup)
console.log('📝 Loading keypairs...');
const userKeypair = await loadKeypair('user-keypair.json');
const recipientKeypair = await loadKeypair('recipient-keypair.json');
console.log(` User: ${userKeypair.address}`);
console.log(` Recipient: ${recipientKeypair.address}\n`);
// Use mint from setup
const usdcMint = address(USDC_MINT_ADDRESS);
console.log(`💵 Using USDC mint: ${usdcMint}\n`);
console.log('✅ Test environment ready!\n');
env = {
rpc,
koraClient,
userKeypair,
recipientKeypair,
usdcMint
};
});
Configuration Tests
This section validates the Kora server configuration and demonstrates the configuration API methods.
// Configuration Tests - Validate Kora server setup
describe('Kora Configuration Tests', () => {
it('should connect to Kora server', async () => {
const config = await env.koraClient.getConfig();
assert.ok(config, 'Should receive config from Kora');
assert.ok(config.fee_payers, 'Config should include fee payers array');
assert.ok(config.fee_payers.length > 0, 'Should have at least one fee payer');
});
it('should return valid fee payer address', async () => {
const config = await env.koraClient.getConfig();
assert.doesNotThrow(
() => address(config.fee_payers[0]),
'Fee payer should be valid Solana address'
);
});
it('should include USDC in allowed tokens', async () => {
const config = await env.koraClient.getConfig();
assert.ok(
config.validation_config.allowed_tokens.includes(env.usdcMint),
'USDC should be in allowed tokens list'
);
assert.ok(
config.validation_config.allowed_spl_paid_tokens.includes(env.usdcMint),
'USDC should be in allowed payment tokens list'
);
});
it('should fetch blockhash from Kora', async () => {
const { blockhash } = await env.koraClient.getBlockhash();
assert.ok(blockhash, 'Should receive blockhash from Kora');
assert.strictEqual(typeof blockhash, 'string', 'Blockhash should be a string');
assert.ok(blockhash.length > 0, 'Blockhash should not be empty');
});
it('should get supported tokens', async () => {
const response = await env.koraClient.getSupportedTokens();
assert.ok(response.tokens, 'Should return tokens object');
assert.ok(Array.isArray(response.tokens), 'Tokens should be an array');
assert.ok(response.tokens.length > 0, 'Should have at least one supported token');
assert.ok(
response.tokens.includes(env.usdcMint),
'USDC should be in supported tokens list'
);
});
it('should get payer signer information', async () => {
const payerInfo = await env.koraClient.getPayerSigner();
assert.ok(payerInfo.signer_address, 'Should return signer address');
assert.ok(payerInfo.payment_address, 'Should return payment address');
assert.doesNotThrow(
() => address(payerInfo.signer_address),
'Signer address should be valid Solana address'
);
});
});
Fee Estimation Tests
This section demonstrates how to estimate transaction fees and convert them to token amounts, which is critical for showing users how much they'll pay before executing a transaction.
The tests first call transferTransaction to build a sample token transfer transaction, and then call estimateTransactionFee with the transaction and the desired payment token. The method returns both fee_in_lamports and fee_in_token so clients can display the cost to users in their preferred denomination.
// Fee Estimation Tests - Calculate transaction costs
describe('Fee Estimation Tests', () => {
it('should estimate fee in lamports', async () => {
// Use Kora's transferTransaction to build a test transaction
const transferResponse = await env.koraClient.transferTransaction({
amount: 1000, // 0.001 USDC
token: env.usdcMint,
source: env.userKeypair.address,
destination: env.recipientKeypair.address
});
// Estimate fee using Kora's estimateTransactionFee method
const { fee_in_lamports } = await env.koraClient.estimateTransactionFee({
transaction: transferResponse.transaction,
fee_token: env.usdcMint
});
assert.ok(fee_in_lamports > 0n, 'Fee should be greater than 0');
assert.ok(fee_in_lamports < 10_000_000n, 'Fee should be less than 0.01 SOL');
});
it('should convert fee to USDC equivalent', async () => {
// Use Kora's transferTransaction to build a test transaction
const transferResponse = await env.koraClient.transferTransaction({
amount: 1000, // 0.001 USDC
token: env.usdcMint,
source: env.userKeypair.address,
destination: env.recipientKeypair.address
});
// Estimate fee using Kora's estimateTransactionFee method
const { fee_in_lamports, fee_in_token } = await env.koraClient.estimateTransactionFee({
transaction: transferResponse.transaction,
fee_token: env.usdcMint
});
const feeInSol = Number(fee_in_lamports) / LAMPORTS_PER_SOL;
const feeInUsdc = Number(fee_in_token) / Math.pow(10, USDC_DECIMALS);
assert.ok(feeInSol > 0, 'Fee in SOL should be greater than 0');
assert.ok(feeInUsdc > 0, 'Fee in USDC should be greater than 0');
// Relaxed for Mock price source (local testing) - production with Jupiter will have realistic fees
assert.ok(feeInUsdc < 10, 'Fee in USDC should be reasonable (< $10 for Mock mode)');
});
});
Gasless Transfer Test
This section contains the end-to-end integration test that executes a complete gasless transaction and verifies it works correctly.
The test first records the user's SOL and USDC balances before the transaction to establish a baseline for verification. It then calls executeGaslessTransfer to build, sign, and broadcast the complete transaction.
After the transaction completes, the test queries the balances again and verifies two critical outcomes:
- The USDC balance decreased by the transfer amount plus the fee
- The SOL balance remained completely unchanged.
// Gasless Transfer Test - End-to-end verification
describe('Gasless Transfer Tests', () => {
it('should execute gasless USDC transfer with fee paid in USDC and SOL balance unchanged', async () => {
const beforeBalances = await getBalances(env.rpc, env.userKeypair.address, env.usdcMint);
console.log('\n💰 Initial balances:');
console.log(` User USDC: ${beforeBalances.usdc.toFixed(4)} USDC`);
console.log(` User SOL: ${beforeBalances.sol.toFixed(2)} SOL\n`);
const transferAmount = 10;
const result = await executeGaslessTransfer({
rpc: env.rpc,
koraClient: env.koraClient,
userKeyPair: env.userKeypair,
recipientAddress: env.recipientKeypair.address,
usdcMint: env.usdcMint,
amount: transferAmount
});
console.log(`\n✅ Transaction: ${result.signature.slice(0, 8)}...${result.signature.slice(-4)}\n`);
const afterBalances = await getBalances(env.rpc, env.userKeypair.address, env.usdcMint);
console.log('📊 Final balances:');
console.log(` User USDC: ${afterBalances.usdc.toFixed(4)} USDC`);
console.log(` User SOL: ${afterBalances.sol.toFixed(2)} SOL (unchanged!)\n`);
// Verify transaction succeeded
assert.ok(result.signature, 'Transaction should have signature');
assert.ok(result.signature.length > 0, 'Signature should not be empty');
// Verify USDC decreased by transfer amount + fee
const expectedDecrease = transferAmount + result.feeInUsdc;
const actualDecrease = beforeBalances.usdc - afterBalances.usdc;
assert.ok(
Math.abs(actualDecrease - expectedDecrease) < 0.02,
`USDC should decrease by transfer + fee (expected: ${expectedDecrease.toFixed(4)}, actual: ${actualDecrease.toFixed(4)})`
);
// Verify SOL balance unchanged (gasless!)
assert.strictEqual(
afterBalances.sol,
beforeBalances.sol,
'User SOL balance should remain unchanged - gasless!'
);
console.log(`✅ Confirmed: USDC decreased by ${actualDecrease.toFixed(4)} (${transferAmount} transfer + ${result.feeInUsdc.toFixed(4)} fee)`);
console.log(`✅ Confirmed: SOL balance unchanged (gasless verified!)\n`);
});
});
Run Tests
With all files created, run the test suite:
npm run test
You should see output like:
✅ Test environment ready!
▶ Kora Configuration Tests
✔ should connect to Kora server
✔ should return valid fee payer address
✔ should include USDC in allowed tokens
✔ should fetch blockhash from Kora
✔ should get supported tokens
✔ should get payer signer information
▶ Fee Estimation Tests
✔ should estimate fee in lamports
✔ should convert fee to USDC equivalent
💰 Initial balances:
User USDC: 1000.00 USDC
User SOL: 0.99 SOL
📝 Constructing transfer: 10 USDC
🔧 Building transaction with Kora
💵 Getting payment instruction from Kora
Fee: 0.0111 USDC
✍️ Building transaction with user signature
📤 Sending to Kora for co-signing and broadcast
✅ Transaction completed successfully
✅ Transaction: 5XqK8G3n...Mv2d
📊 Final balances:
User USDC: 989.99 USDC
User SOL: 0.99 SOL (unchanged!)
✅ Confirmed: USDC decreased by 10.0111 (10 transfer + 0.0111 fee)
✅ Confirmed: SOL balance unchanged (gasless verified!)
▶ Gasless Transfer Tests
✔ should execute gasless USDC transfer with fee paid in USDC and SOL balance unchanged
ℹ tests 9
ℹ pass 9
If all tests pass, congratulations! You've successfully configured a Kora RPC server and executed a gasless transaction where users paid fees in USDC instead of SOL.
Sponsored Transactions
While gasless transactions let users pay with tokens other than SOL, you can take this a step further by sponsoring transaction fees entirely. Instead of users paying fees in USDC or other tokens, your application covers all transaction costs, creating a completely free experience for end users.
Kora makes sponsored transactions easy to implement. You only need two configuration changes in kora.toml:
Empty SPL Payment Tokens:
allowed_spl_paid_tokens = []
Free Pricing:
[validation.price]
type = "free"
# margin = 0.1
Sponsored Transfer Test
This test demonstrates fully sponsored transactions where your application covers all transaction costs and users pay nothing. The key difference from the gasless transfer test is the absence of the getPaymentInstruction call.
The test verifies two critical outcomes:
- The USDC balance decreases by exactly the transfer amount with no additional fee deducted
- The SOL balance remains completely unchanged, confirming the transaction is both sponsored and gasless
describe('Sponsored Transfer', () => {
it('should transfer USDC without charging any fees', async () => {
const beforeBalances = await getBalances(env.rpc, env.userKeypair.address, env.usdcMint);
const transferAmount = 10;
console.log(`\n💰 Initial balances:`);
console.log(` User USDC: ${beforeBalances.usdc.toFixed(4)} USDC`);
console.log(` User SOL: ${beforeBalances.sol.toFixed(2)} SOL\n`);
// Build transfer transaction
console.log(`📝 Building sponsored transfer: ${transferAmount} USDC`);
const transferResponse = await env.koraClient.transferTransaction({
amount: transferAmount * Math.pow(10, USDC_DECIMALS),
token: env.usdcMint,
source: env.userKeypair.address,
destination: env.recipientKeypair.address
});
// KEY: In sponsored mode, skip getPaymentInstruction() - no fee charged
const allInstructions = transferResponse.instructions;
// Get fresh blockhash with lastValidBlockHeight from RPC
// Kora's transferResponse only has blockhash string, not lastValidBlockHeight
const latestBlockhash = await env.rpc.getLatestBlockhash().send();
const noopSigner = createNoopSigner(address(transferResponse.signer_pubkey));
// Build and sign transaction
const txMessage: any = allInstructions.reduce(
(tx: any, instruction: any) => appendTransactionMessageInstruction(instruction, tx),
pipe(
createTransactionMessage({ version: 0 }),
tx => setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner(noopSigner, tx),
tx => setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash(latestBlockhash.value, tx)
)
);
const partiallySigned = await partiallySignTransactionMessageWithSigners(txMessage);
const userSigned = await partiallySignTransaction([env.userKeypair.keyPair], partiallySigned);
const signedTxBase64 = getBase64EncodedWireTransaction(userSigned);
// Send to Kora for co-signing and broadcast
console.log(`📤 Sending to Kora for signing and broadcast`);
await env.koraClient.signAndSendTransaction({ transaction: signedTxBase64 });
console.log(`✅ Transaction completed\n`);
const afterBalances = await getBalances(env.rpc, env.userKeypair.address, env.usdcMint);
const usdcDecrease = beforeBalances.usdc - afterBalances.usdc;
console.log(`📊 Final balances:`);
console.log(` User USDC: ${afterBalances.usdc.toFixed(4)} USDC (${usdcDecrease.toFixed(4)} decrease)`);
console.log(` User SOL: ${afterBalances.sol.toFixed(2)} SOL (unchanged)\n`);
// Verify: User paid ONLY transfer amount (no fee in USDC)
assert.strictEqual(usdcDecrease, transferAmount, 'USDC should decrease by exact transfer amount only');
// Verify: SOL balance unchanged (no fee in SOL)
assert.strictEqual(afterBalances.sol, beforeBalances.sol, 'SOL balance should remain unchanged');
});
});
After updating kora.toml to enable sponsored mode, restart your Kora server to apply the configuration changes:
kora rpc start --signers-config signers.toml
Since the configuration now uses sponsored mode instead of user-paid mode, some of the original tests will fail because they expect fees to be charged in USDC. To keep testing simple and focused on the sponsored transaction behavior, we'll skip those incompatible tests.
In test/gasless-transfer.test.ts, add describe.skip() to disable these test suites:
// Skip entire Configuration Tests suite as they're not relevant to sponsored mode.
describe.skip('Kora Configuration Tests', () => {
// All tests check for user-paid config
});
// Skip entire Fee Estimation Tests suite as they're not relevant to sponsored mode.
describe.skip('Fee Estimation Tests', () => {
// These try to estimate fees with fee_token parameter
// Fails because USDC isn't in allowed_spl_paid_tokens
});
// Skip entire Gasless Transfer Tests suite as they're not relevant to sponsored mode.
describe.skip('Gasless Transfer Tests', () => {
// Tests user-paid mode where fees ARE charged in USDC
});
Run Sponsored Test
After updating kora.toml to enable sponsored mode, restart your Kora server to apply the configuration changes:
kora rpc start --signers-config signers.toml
Then run the sponsored transaction test to verify that transactions complete successfully with all fees covered by your application:
npm run test
When the test runs successfully, you'll see the following output:
Initial balances:
User USDC: 915.0000 USDC
User SOL: 5.00 SOL
📝 Building sponsored transfer: 10 USDC
📤 Sending to Kora for signing and broadcast
✅ Transaction completed
📊 Final balances:
User USDC: 905.0000 USDC (10.0000 decrease)
User SOL: 5.00 SOL (unchanged)
Security Considerations
As of January, 2026, Kora uses the unaudited solana-keychain package. While Kora v2.0.3 has been audited by Runtime Verification through commit 8c592591, conduct additional security review for production mainnet deployments.
When deploying to production, transition from file-based keypairs to a secure key management service:
- Turnkey: Enterprise-grade key management with hardware security modules (HSMs) and policy controls for granular access management
- Privy: Embedded wallet infrastructure with secure key management designed specifically for Web3 applications
- Vault: HashiCorp Vault integration for enterprise environments requiring centralized secrets management
For complete configuration examples and required credentials for each provider, see the official Kora signers documentation.
Review your program allowlist carefully to only include programs your application legitimately needs to call. If you're unsure whether a program is necessary, monitor your application's transactions and add programs only when you see validation failures for legitimate operations.
Advanced Features
Kora provides several advanced features for production deployments:
- Token Extensions Support: Full support for Token Extensions, also known as Token-2022 extensions including transfer fees, permanent delegates, and interest-bearing tokens
- Performance Optimization: Redis caching improves response times for frequently accessed data like token prices and account states
- Rate Limiting: Protect against abuse with per-account spending limits and transaction frequency caps
- Enhanced Fee Payer Protection Policies: Fine-tuned control over spending patterns, transaction types, and account-level restrictions with tiered user systems
- Multiple Signers: Route transactions across multiple fee payer accounts with configurable strategies (round-robin, threshold-based, etc.)
Run Your Own Kora Node
To operate a Kora node, you need a fee payer signer and you must keep it funded with enough SOL to sponsor the transactions you approve. This gives you control over which tokens you accept, enables fully sponsored transactions, and lets you set your own policies like rate limits, validation rules, and authentication.
At a high level, deployment is installing the Kora CLI with your kora.toml and signers.toml, pointing the node to a Solana RPC endpoint, and starting the Kora server. You can run locally for testing, deploy via Docker (optionally with Redis caching), or use a hosted flow like Railway.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if my fee payer account runs out of SOL?
When your fee payer balance drops too low, Kora will fail to sign new transactions because Solana requires fee payers to have sufficient balance to cover transaction costs. Monitor your fee payer balance using Kora's metrics and set up alerts when it drops below a threshold.
Can users still pay fees with SOL if they want to?
Yes. Kora is an optional service for your users. You can build your client to detect whether users have sufficient SOL and, if so, allow them to pay fees traditionally without involving Kora. Your client logic determines which flow to use based on the user's token holdings and preferences.
How do I handle token price volatility?
Configure a margin in your pricing settings to add a buffer above the actual SOL cost. For example, a 10% margin means users pay 10% more in token value than the SOL cost, protecting you from price fluctuations between when you quote the fee and when the transaction executes. For production deployments, use Jupiter's price oracle (price_source = "Jupiter") to get real-time market prices instead of mock pricing. You can also limit which tokens you accept to stablecoins or blue-chip tokens with deeper liquidity and less volatility.
Is Kora suitable for high-frequency applications?
Kora adds minimal latency of one RPC round trip for transaction signing. For most applications, this overhead is negligible compared to network latency and Solana's block time.
Can I use multiple signers with different security levels?
Yes. Configure multiple signers in signers.toml and define a selection strategy. For example, you might route high-value transactions to a more secure but slower signer backed by Turnkey or implement a round-robin selection to distribute spending across multiple fee payer accounts to avoid per-account rate limits.
Wrapping Up
You've successfully built a complete gasless transaction system from scratch! More importantly, you understand Kora's architecture: how it validates transactions before signing, how it fits between your client and the Solana network, and how it enables business models impossible with traditional fee payment.
Try offering sponsored transactions for new users' first five interactions. Test accepting your native token as payment, creating direct token utility. Implement tiered fee structures where different user segments pay different amounts. Kora gives you the flexibility to iterate on fee models without changing your core application logic. You only need to update Kora's configuration.
Resources
- Kora GitHub Repository - Kora source code
- Kora Introduction - Official Kora docs
- Kora Quick Start Guide - Getting started tutorial
- Kora Operators Documentation - Running a Kora node
- @solana/kora Package - TypeScript SDK for client integration
- Kora CLI - Rust crate for running a Kora node
- Turnkey - HSM-backed secure key management
- Privy - Embedded wallet infrastructure
- Vault - HashiCorp Vault integration
We ❤️ Feedback!
Let us know if you have any feedback or requests for new topics. We'd love to hear from you.